Prompt Tuning Vision Language Models is Robust to Noisy Labels
Abstract
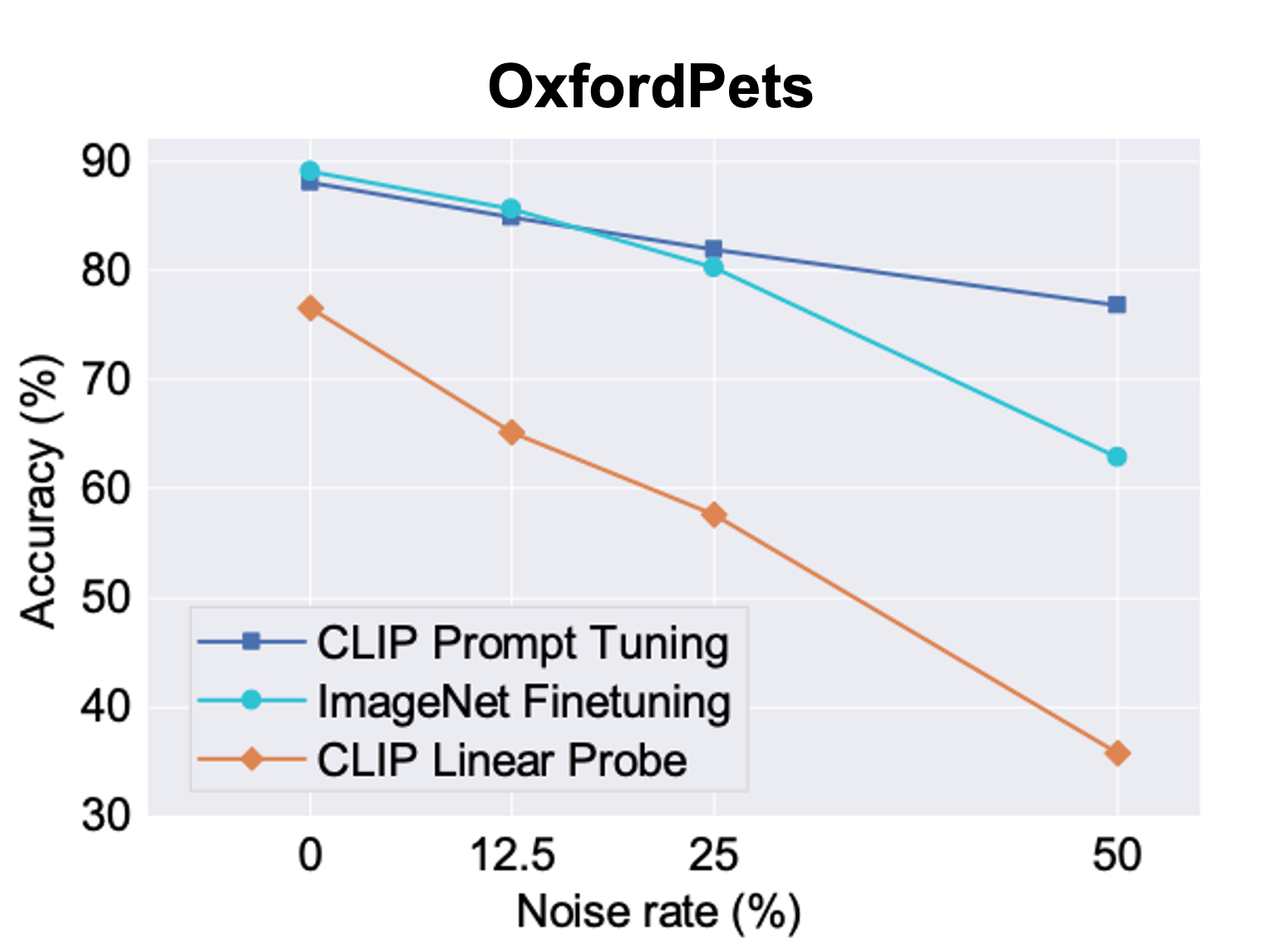
Vision-language models such as CLIP learns a generic text-image embedding from large-scale of training data. A vision-language model can be adapted to a new classification task through few-shot prompt tuning. We find that such prompt tuning process is highly robust to label noises. This intrigues us to study the key reasons contributing to the robustness of the prompt tuning paradigm. We conducted extensive experiments to explore this property and find the key factors are: 1. the fixed classname tokens provide a strong regularization to the optimization of the model, reducing gradients induces by the noisy samples; 2. the powerful pre-trained image-text embedding that is learned from diverse and generic web data provides strong prior knowledge for image classification. Further, we demonstrate that noisy zero-shot predictions from CLIP can be used to tune its own prompt, significantly enhancing prediction accuracy in the unsupervised setting.
Published at: International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, 2023.
Bibtex
@InProceedings{wu2023_robust_pt,
title={Why Is Prompt Tuning for Vision-Language Models Robust to Noisy Labels?},
author={Cheng-En Wu, Yu Tian, Haichao Yu, Heng Wang, Pedro Morgado, Yu Hen Hu, Linjie Yang},
booktitle={International Conference in Computer Vision (ICCV)},
year={2023}
}